Theme: Therapeutic Interventions Including Development and Clinical Trials of Drugs
EURO CLINICAL TRIALS 2022
The main target is to bring all the leading academic scientists, researchers, and research scholars together to exchange and share their experiences and research results about Clinical Research and Clinical trials. It also provides the leading interdisciplinary forum for researchers and educators to present and discuss the top recent innovations, trends, and concerns, practical challenges run into and the solutions acquire within the field of Clinical Research and Clinical trials. The conference program will cover a good variety of topics relevant to Observational studies or epidemiology and Interventional studies or Clinical trials.
Intended authors are encouraged and help to shape the conference through submissions of their research abstracts, papers, and e-posters. Also, high-quality research present report original and unpublished results of conceptual, experimental, or thesis work in all areas of Clinical Research and Clinical Trials are cordially invited for presentation at the conference. The conference solicitation for contributions of abstracts, papers, and e-posters that address themes and topics of the conference, including figures, and references research materials.
Track 1: Clinical Research
Refers to all or any research carried out on humans. It focuses on improving understanding of diseases, developing diagnostic methods and new treatments or medical devices to make sure better patient care. It’s much framed and a particular study protocol and is merely realized under certain conditions.
(A) Pre-Clinical Research: Before testing a drug in people, researchers must find out whether it has the potential to cause serious harm, also called toxicity. The two types of preclinical research are:
- In Vitro
- In Vivo
These researches set the minimum basic requirements for:
- study conduct
- personnel
- facilities
- equipment
- written protocols
- operating procedures
- study reports
Track 2: Clinical trials
These are research studies perform on people that are aimed toward evaluating a medical, surgical, or behavioral intervention. They’re the first way that researchers determine if a replacement treatment, like a new medicine or diet, or medical device is safe and effective in people. Often a clinical test is employed to find out if a replacement treatment is simpler and/or has less harmful side effects than the standard treatment.
(A) Clinical Study Designs: Clinical study design is the formulation of trials and experiments, as well as observational studies in medical, clinical and other types of research (e.g., epidemiological) involving human beings. The goal of a clinical study is to assess the safety, efficacy, and / or the mechanism of action of an investigational medicinal product or procedure, or new drug or device that is in development, but potentially not yet approved by a health authority (e.g. Food and Drug Administration).It can also be to investigate a drug, device or procedure that has already been approved but is still in need of further investigation, typically with respect to long-term effects or cost-effectiveness.
Track 3: Prevention trials
Prevention Trials search for ways to prevent disease in people that haven't had the disease or to stop a disease from returning.
(A) Patient-Centric Clinical Trials: “Patient centricity” means designing a treatment, clinical trial, or other health solution centered on the patient. Creating a patient-centric solution involves getting feedback from real patients and their loved ones, and making decisions based on their needs and perspectives.
Track 4:Screening trials
Screening trials test for tactics to spot unquestionable diseases or health conditions.
(A) Innovations in clinical Trials: Aspects of clinical trials that were once thought to be clunky and inconsistent such as patient recruitment have now been streamlined and made much more efficient through the use of digital technology. In fact, all phases of drug development have been impacted by the use of innovative new technology from protocol optimization leveraging advanced data and analytics to enhancing patient retention through virtual clinical trials and the use of real-world data in post approval studies.
Track 5:Diagnostic trials
Diagnostic trials are performed to find better procedures for diagnosing a specific disease.
(A) Patient Recruiting Retention: Recruiting and enrolling patients for clinical trials can often be a long and difficult process. It’s not surprising then, that finding the target demographic, qualifying and enrolling patients can consume valuable time and money. Therefore, it is imperative that the process of recruiting is well planned and fits within the protocol budget and timeline. Once patients are enrolled in a study, it can be just as hard to retain them. A variety of unexpected factors can lead patients to withdraw from the study, resulting in inadequate data and potentially, a costlier trial.
Track 6:Treatment trials
Treatment trials test experimental medicine, new combinations of medicine, or new approaches to surgery or radiotherapy.
(A) Clinical Data Management and Statistics: Clinical data management (CDM) is the process of collecting and managing research data in accordance with regulatory standards to obtain quality information that is complete and error-free. The goal is to gather as much of such data for analysis as possible that adheres to federal, state, and local regulations.
Track 7:Quality of life trials
Quality of life trials evaluate the way to improve relief and quality of look after people with a chronic illness.
(A) Clinical and Medical Case Reports: A case report is a detailed report of the symptoms, signs, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of an individual patient. Case reports usually describe an unusual or novel occurrence and as such, remain one of the cornerstones of medical progress and provide many new ideas in medicine.
Track 8:Genetic trials
Genetic trials are conducted to assess the projection accuracy of genetic disorders making a person more or less likely to develop a disease.
(A) Pharmacovigilance and Drug Safety: Pharmacovigilance (PV, or PhV), also known as drug safety, is the pharmacological science relating to the collection, detection, assessment, monitoring, and prevention of adverse effects with pharmaceutical products.
Track 9:Epidemiological trials
Epidemiological trials have the goal of spot the overall causes, patterns, or control of diseases in large numbers of individuals.
(A) Data management in Pharmacovigilance: The Pharmacovigilance data processing cycle starts with data collection and, in computerized systems, data entry; the next step is data storage and maintenance; followed by data selection, retrieval and manipulation. The resulting data outputs analyzed and assessed. Finally, conclusions are drawn and decisions made.
Track 10:Compassionate use trials or expanded access trials
Compassionate use trials or expanded access trials provide partially tested, unapproved therapeutics to a little number of patients who haven't any other realistic options. This requires a disease that no effective therapy has been approved or a patient who has already failed all standard treatments and whose health is too compromised to qualify for a part in randomized Clinical trials.
(A) Drug Discovery and Development: Drug discovery and development together are the complete process of identifying a new drug and bringing it to market. Discovery may involve screening of chemical libraries, identification of the active ingredient from a natural remedy or design resulting from an understanding of the target. Development includes studies on microorganisms and animals, clinical trials and ultimately regulatory approval.
Track 11:Fixed trials
Fixed trials consider existing data only during the trial's design, predicting to not assess the results until the study is completed.
(A) CRO or Sponsorship Clinical Trials: A CRO (Contract Research Organization) is a company that provides clinical trial management services for the pharmaceutical, biotech, and medical device industries. Although there are different types of CROs and diverse levels of specialization (distinct therapeutic areas for instance), typical CRO services include regulatory affairs, site selection and activation, recruitment support, clinical monitoring, data management, trial logistics, Pharmacovigilance, biostatistics, medical writing, and project management, among others.
Track 12:Controlled Clinical Trials – Aims and Designs
Controlled Clinical Trials use existing data to style the trial, then use interim results to switch the trial because it proceeds. It covers dosage, sample size, drug undergoing trial, patient selection criteria. These trials often appoint a Bayesian experimental design to assess the trial's progress. In some cases, trials have become an ongoing process that often adds and drops therapies and patient groups as more information is gained. The only point is to more quickly identify drugs that have healing.
(A) Bioethics and Quality Regulation: “Bioethics” is a term with two parts, and each needs some explanation. Here, “ethics” refers to the identification, study, and resolution or mitigation of conflicts among competing values or goals. The ethical question is, “What should we do, all things considered?” The “bio” puts the ethical question into a particular context. Bioethics is commonly understood to refer to the ethical implications and applications of the health-related life sciences. These implications can run the entire length of the bench-to-bedside “translational pipeline.” Dilemmas can arise for the basic scientist who wants to develop synthetic embryos to better study embryonic and fetal development, but is not sure just how real the embryos can be without running into moral limits on their later destruction.
Track 13:Randomized controlled trials or Aimless trials
Aimless or randomized controlled trials that aims to reduce certain sources of partiality when testing the effectiveness of new treatments; this is accomplished by randomly allocating subjects to two or more groups, treating them differently, and then collate them with respect to a measured response.
(A) Post-marketing Surveillance: Post marketing surveillance is the monitoring of drug performance in clinical practice and the taking of appropriate action to improve patient safety. The action taken can range from changes in product labeling (e.g., dose regimen alterations, drug interaction alerts, and warnings about previously unknown adverse effects) to product withdrawal from the market. The changes can be instituted either voluntarily by the drug companies concerned or enforced through regulatory action.
Track 14:Blind trial
Blind trial in this the information which may influence the participants of the experiment after the experiment is complete. Good blinding can reduce or eliminate experimental cross that arises from a participant's expectations, observer's effect on the participants, observer cross, confirmation bias, and other sources. A blind trial can be imposed on any member of an experiment, including subjects, researchers, technicians, data analysts, and evaluators. For example, it is not possible to unsighted a patient to their treatment in a physical therapy intervention.
(A) Research and Trials on Oncology and AIDS: Interpretation of clinical trials to guide therapy for those with HIV infection and cancer largely depends on data that does not include HIV-infected patients. The ability to extend clinical trial findings to populations not included in clinical trials remains problematic for a variety of populations, including those with HIV or AIDS. Careful prioritization of studies designed to bridge this gap is needed. However, there are published studies that serve as excellent examples bridging these gaps and the portfolio of cancer therapy trials underway will inform HIV and cancer better than at any time in the past.
Track 15:Non-blind trial an open-label trial
Non-blind trial an open-label trial is a type of clinical trial in which information is not holding back from trial participants. In particular, the researchers and participants know which treatment is being managed. This contrasts with a double-blinded trial, where information is holdback both from the researchers and the participants to scale back bias.
(A) Globalization of Clinical Trials: The globalization of clinical trials can bring both health benefits and hazards to research subjects and the general population. Potential benefits include diffusion of medical knowledge and effective medical practice, and greater patient access to high quality medical care.
Track 16:Adaptive clinical
Adaptive clinical test an adaptive clinical test may be a clinical test that evaluates a medical device or treatment by observing participant outcomes on a prescribed schedule and modifying parameters of the trial protocol in accordance to observations.
(A) Clinical Trial Site Selection and Management: These three steps should take place in order to ensure an optimal site selection. In the industry we often hear staggering statistics about the number of trials that are delayed or fail to meet their goals. For example, you may have heard 45% of clinical trials are completed late, 70% of trials experience study start-up delays1, and approximately 80% of trials fail to meet their initial target enrollment on time.
Step 1: Define Site Requirements and Selection Criteria
Step 2: Identify Sites and Gather Initial Information
Step 3: Evaluate and Select the Sites
Track 17:Nonrandomized trial a quasi-experiment
Nonrandomized trial a quasi-experiment is an observed interventional study used to estimate the causal impact of an intervention on a target population without random assignment. Quasi-experimental research shares similarities with the normal experimental design or randomized controlled trial, but it specifically lacks the element of random assignment to treatment or control. Instead, quasi-experimental designs typically allow the researcher to regulate the assignment to the treatment condition but using some criterion aside from random assignment.
(A) Clinical Trial Forecasting, Budgeting and Contracting: As clinical trials become more complex and take on innovative designs, it is more critical than ever to develop proper strategies for forecasting, budgeting, negotiating, and contracting both internally and externally with sites, CROs, and other partners. Finance and operations teams must continue to evolve and adapt, especially in light of new and changing regulations and laws. Cambridge Healthtech Institute’s 9th Annual “Clinical Trial Forecasting, Budgeting and contracting” conference shares case studies and best practices on effective budgets and clear contracts, as well as metrics and key performance indicators of their success.
Track 18:Project Management and Conduct of Trials
Project Management and Conduct of Trials a method of statistical analysis involving tracking a long-term period before and after some extent of intervention to assess the intervention's effects. The statistic refers to the info over the period, while the interruption is that the intervention, which may be a controlled external influence or set of influences. Effects of the intervention are evaluated by changes within the level and slope of the statistic and therefore the statistical significance of the intervention parameters.
(A) Biomedical Devices Clinical Research: A large number of clinical trials for new medical devices, as well as pharmaceutical / drug trials. In general, the approach to testing devices is fairly similar to testing new drugs – there is a need for preclinical research, there are strict regulations, safety and ethical requirements, and the testing process is broken up into a series of phases/stages. Our previous article, “Introduction to Clinical Trials”, provides an overview of these topics and more. There are, however, some obvious differences when conducting clinical trials for medical devices, compared to pharmaceutical trials, which we will describe here.
Track 19:Clinical Research in nursing
Clinical Research in nursing a practice with a specialty focus on Clinical research. It includes care provided to research participants, as well as activities to support protocol implementation, data collection, and research participant protection. In addition to providing and coordinating clinical care, clinical research nurses have a central role in assuring ongoing maintenance of informed agreement, the integrity of protocol procedures, and the accuracy of research data collection.
(A) Imaging Research Clinical Research Nursing: Clinical research nursing is defined as clinical nursing practice with a specialty focus on research implementation and the care of subjects participating in clinical research. In addition to providing and coordinating clinical care, clinical research nurses have a central role in ensuring participant safety, ongoing maintenance of informed consent, integrity of protocol implementation, accuracy of data collection, and data recording, and follow-up.
Track 20:Clinical Research in Oncology & Cancer trials
Clinical Research in Oncology & Cancer trials is the final step in a long process that begins with research in a lab. Before any new treatment is employed with people in Clinical trials, researchers work for several years to know its effects on cancer cells within the lab and in animals. They also attempt to figure out the side effects it's going to cause.
(A) Oncology Clinical Research: Clinical trials are research studies that involve people. Through clinical trials, doctors find new ways to improve treatments and the quality of life for people with disease. Researchers design cancer clinical trials to test new ways to:
Treat cancer
Find and diagnose cancer
Prevent cancer
Manage symptoms of cancer and side effects from its treatment
Track 21:Clinical Trials in Pharmacy
Clinical Trials in Pharmacy Refers to Investigational which trial a new medicine or an existing medicine for a different condition. The study can assess what doses should be given, how well the drug works in a population, how it works within the body, and any unwanted side effects. This enables a better understanding of trial drugs and wider access for patients to drugs for a given condition. The future of Clinical trials is changing as we glance to advanced therapies which include gene therapy, cell therapy, or any tissue-engineered product. Clinical trial drugs need to be securely managed with detailed accounts maintained concern to their storage, dispensing, return, and destruction. Clinical trial-trained personnel are required to manage these medicines and therefore the specific records require to be completed.
(A) Regulatory affairs: The regulatory affairs (RA) department of a pharmaceutical company is responsible for obtaining approval for new pharmaceutical products and ensuring that approval is maintained for as long as the company wants to keep the product on the market.
Track 22:Immunology in Clinical Research and Clinical Trial
Immunology in Clinical Research and Clinical Trial It is a branch of medical science that covers the study of all aspects of the immune system in all organisms It deals with the physiological functioning of the system in states of both health and diseases. It gives the reader a complete picture of the diverse field of immunology and the excellence of innovative research works. This broad perspective makes Trends in Immunology an important information source for researchers, students, medical practitioners, lab professionals, academicians, and therefore the industry that's involved in Medical and clinical research.
(A) Clinical Trials Auditing: A clinical trial audit is meant to ensure: Protection of subjects enrolled in clinical trials; Increase confidence that the data collected and subsequently submitted is valid; Verify compliance with regulations which includes the principles of Good Clinical Practices (GCPs).
Track 23:Clinical Research and Clinical Trial in Vaccines
Clinical Research and Clinical Trial in Vaccines is a three-phase process. During the phase, I clinical trial, small groups of individuals receive the trial vaccine. In phase II clinical trial, the clinical study is expanded and the vaccine is given to people that have characteristics almost like those for whom the new vaccine is meant. In phase III clinical trial, the vaccine is given to thousands of individuals and tested for efficacy and safety.
Many vaccines undergo phase IV Clinical trials formal, ongoing studies after the vaccine is approved and licensed.
• Exploratory stage
• Pre-clinical stage
• Clinical development
• Regulatory review and approval
• Manufacturing
• Quality Control
(A) Medical Device Research: A medical device is defined, in part, as any health care product that does not achieve its primary intended purposes by chemical action or by being metabolized. An investigational medical device is one that is the subject of a clinical study designed to evaluate the effectiveness and/or safety of the device.
Track 24:Clinical Trial in nutrition
Clinical Trial in nutrition rails of nutritional intervention in a wide range of health and disease states, preventive and therapeutic, are required. Not only has the emergence of chronic non-communicable disease (CNCD) with acknowledged nutritional pathogenesis created this imperative need, but so even have other conditions which, previously, had not been regarded as nutritionally based.
(A) Clinical Research Informatics: Clinical research informatics (CRI) is a subdomain of biomedical and health informatics that focuses on the application of informatics to the discovery and Management of new knowledge relating to health and disease.
Track 25:Clinical Research in pathology
Clinical Research in pathology investigative diagnostic, prognostic, and biomarker studies with clear clinical relevance that promotes our understanding of the mechanisms of human disease. In general, hypothesis-driven studies that are appropriately powered and validated are going to be preferred. As well as original research papers, the Journal seeks to supply rapid publication during a sort of other formats, including editorials, review articles and other features, both contributed and solicited.
(A) Translational and Experimental Clinical Research: In the field of biomedicine, it is often called "translational medicine", defined by the European Society for Translational Medicine as "an interdisciplinary branch of the biomedical field supported by three main pillars: bench side, bedside and community", from laboratory experiments through clinical trials, to therapies.
The world Clinical research and Clinical trials market record was estimated at USD 44.3 billion in 2020 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate of 5.7% from 2021 to 2028. However, the market growth was hampered in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Nevertheless, the future seems promising for the market because of factors like globalization of Clinical trials, rapid technological evolution, and augmenting demand to conduct research activities. The increasing prevalence of long-term disease and the growing demand for Clinical trials in developing countries also boost this market’s growth. The market is also driven by a rising number of biologics, the necessity for personalized medicines and orphan drugs, and demand for advanced technologies.
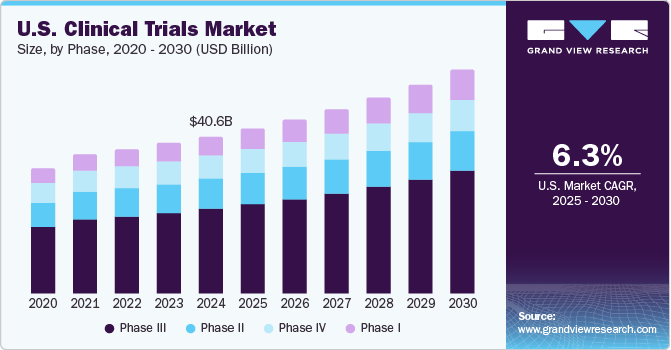
The rapidly evolving threat due to the outbreak of COVID-19 is impacting lives, communities, businesses, and industries around the globe. The pandemic also negatively impacted the ecosystem of clinical trials during the first half of 2020. It affected many ongoing clinical trials for various therapeutic areas. However, to overcome this, researchers developed innovative therapeutics and vaccines against COVID-19, which has supported the market recovery and growth.
Primary goal of attending an international conference is to present a paper to the experts and influencers. It gives you a platform to exchange your interest-related thoughts, paving the way for possible future collaborations. This is a great platform to connect with your peers. Also attending a conference gives you opportunity to get your abstract or paper published in conference proceedings. Meet and greet a myriad of industry professionals and academia experts with common interest. Every meal will be an opportunity to meet and interact with fellow researchers, attendees and experts.
Expand your professional competency and learn useful tips and tricks of your industry in our skill-building workshops. Explore insights on recent advancements, new equipment, new techniques, and unpublished data, learn from thought-leaders and get to network with a great line up of speakers. Investing in you is the best investment. Peers Alley conferences give the patrons with a feeling of the serendipity of real learning, skill development in strategic workshops, networking and start-up opportunities, thus, is value for money.
Conference Highlights
- Clinical Research
- Clinical trials
- Prevention trials
- Screening trials
- Diagnostic trials
- Treatment trials
- Quality of life trials (supportive care trials)
- Genetic trials
- Epidemiological trials
- Compassionate use trials or expanded access trials
- Fixed trials
- Randomized controlled trial
- Blind trial
- Non-blind trial an open-label trial, or open trial
- Non randomized trial (quasi-experiment)
- Clinical Research and Clinical Trial in Vaccines
- Clinical Research in Nursing
- Clinical Research in Oncology & Cancer
- Clinical Trials in Pharmacy
- Immunology in Clinical Research and Clinical Trial
- Clinical Research and Clinical Trial in Vaccines
- Clinical Trial in nutrition
- Clinical Research in Pathology
- Project Management and Conduct of Trials
- Controlled Clinical Trials – Aims and Designs
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | September 05-06, 2022 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by
